Modularization
In ABAP, you can modularize your code with 3 different ways, subroutine, include, and function module.
| Method | Availability | Accept Parameters | Access to Program variables | Expose its Variables to Program |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Subroutine | only within the same program | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Include | Can be accessed globally in any program | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ |
| Function Module | Can be accessed globally in any program | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
Define a Subroutine
FORM writeData.
write: / 'Name', lv_name.
"... many statements
ENDFORM
This code block can be called anywhere in the same program using:
PERFORM writeData.
This will execute the code-block written in the subroutine.
Define an Include
excatly same process of create a Z_Program, with one minor difference.
When creating the TYPE should be INCLUDE PROGRAM instead of EXECUTE PROGRAM
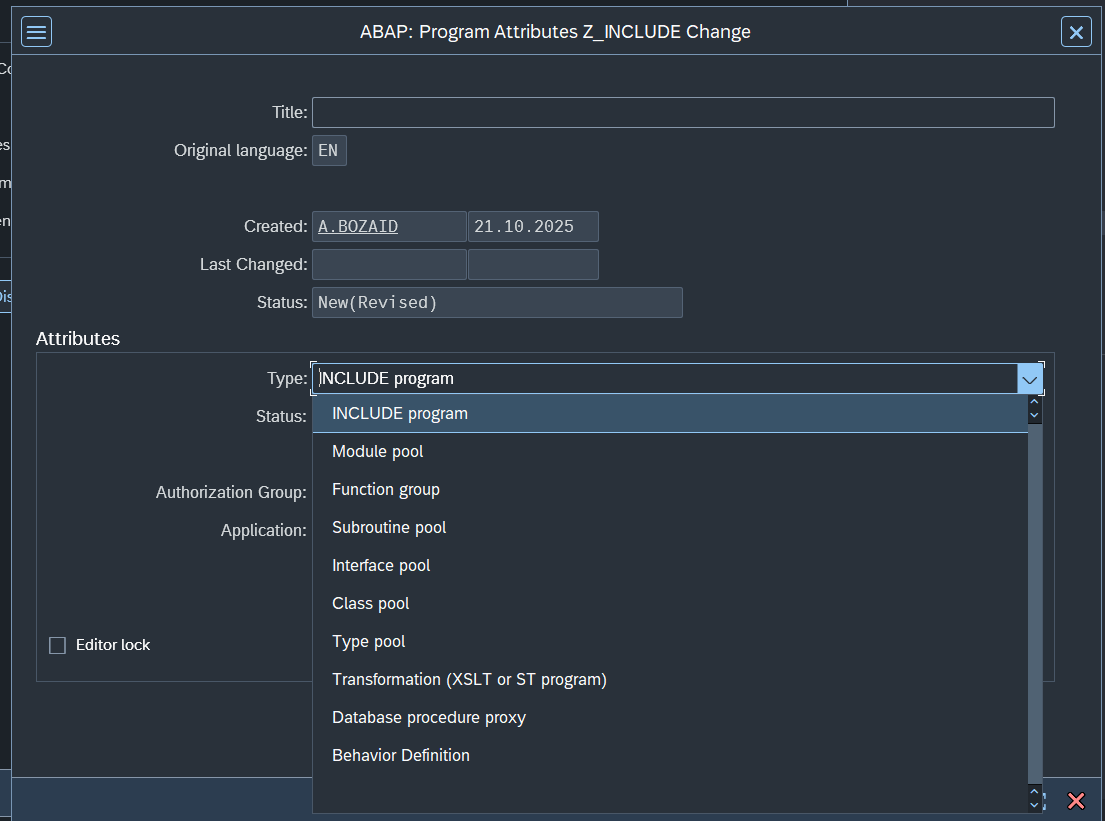
Should be like this after creating it.
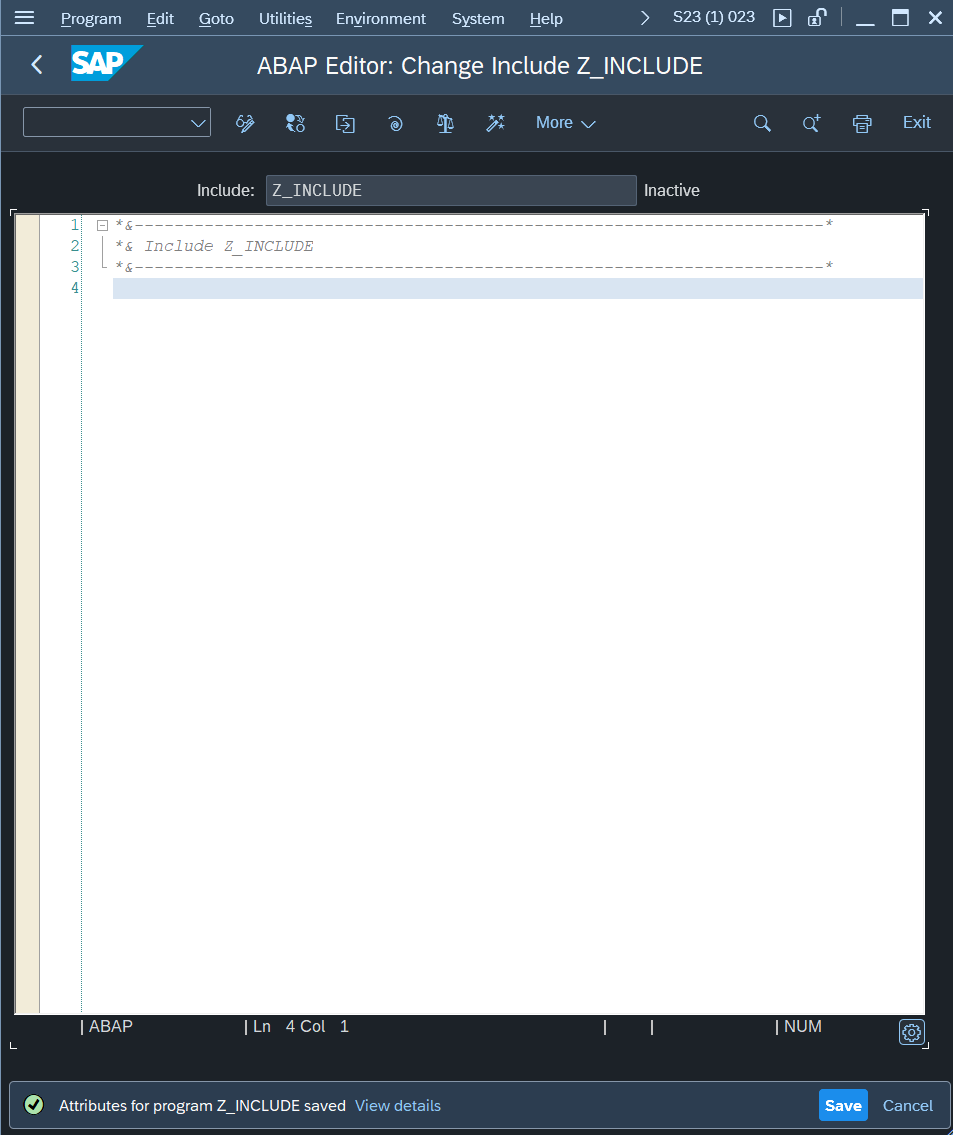 Note we define a variable here and printed a statement from the Include.
Note we define a variable here and printed a statement from the Include.
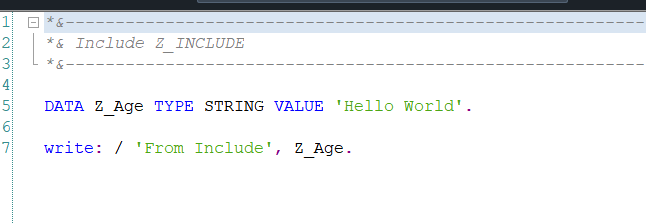 Here we didnt define a Z_Age in our program. but we can write it. Since include expose its variables to the program.
Here we didnt define a Z_Age in our program. but we can write it. Since include expose its variables to the program.
Note the print statements
Define Function Module
Pre-requisite
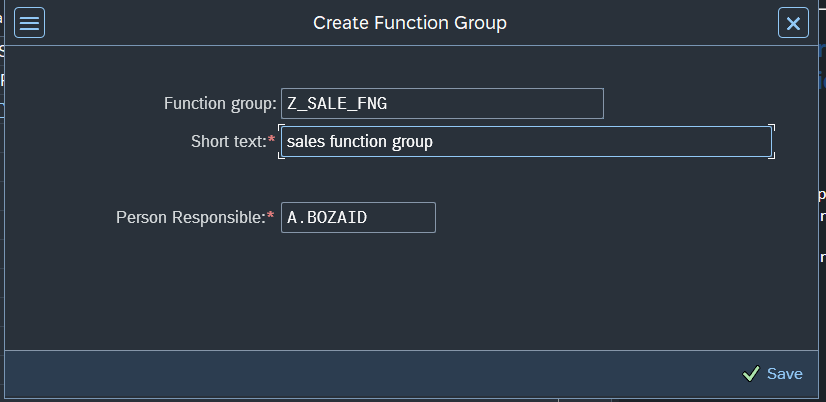
before we create a Function Module, we first need to create a function group from SE80 Transaction.
We select Function Group and write our function group name.
Then we click on the Binocular 🕶️.
 Provide a description and click ✅ Save.
Provide a description and click ✅ Save.
You will be prompted to select the package, and request similar to creating a program.
Creating the Function Module
You can create a function module using the SE37 Transaction.
Fill the name and click on Binocular 🕶️2
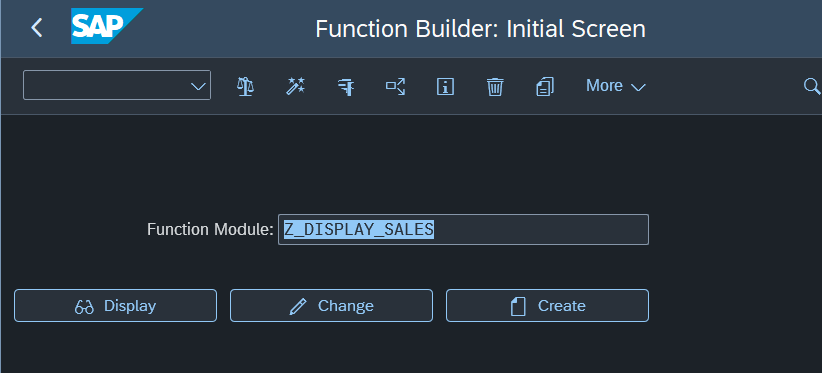
Choose the function group you created previously and add short text as description
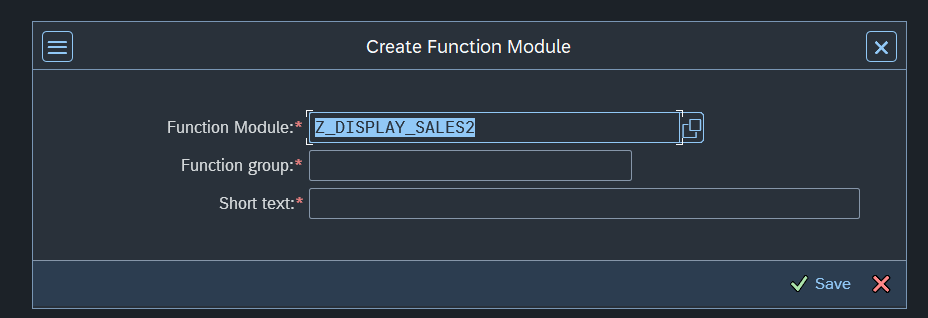
After Creation you will see many options (Import, Export, Source Code...etc) We will discuss them one by one.

Import
Here you define the parameters that should be passed to the function.
These will be provided later on when you call the function from the program.
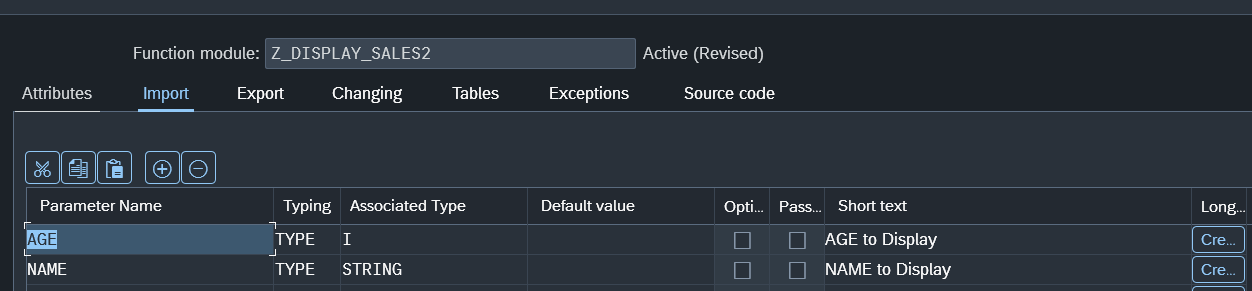
Here we can see that the function Accepts two imports (aka parameters). We need to define the data elements that they accepts. Here we choose a integer and a string.
Export
Here you define the variables that should be exported or returned to from the function call.
You can consider these variables as defined before hand. You can use them directly or assign a value to them.

Testing Function module
You can try the function module by clicking F8
It will navigate to this view. Here you can provide sample data and click
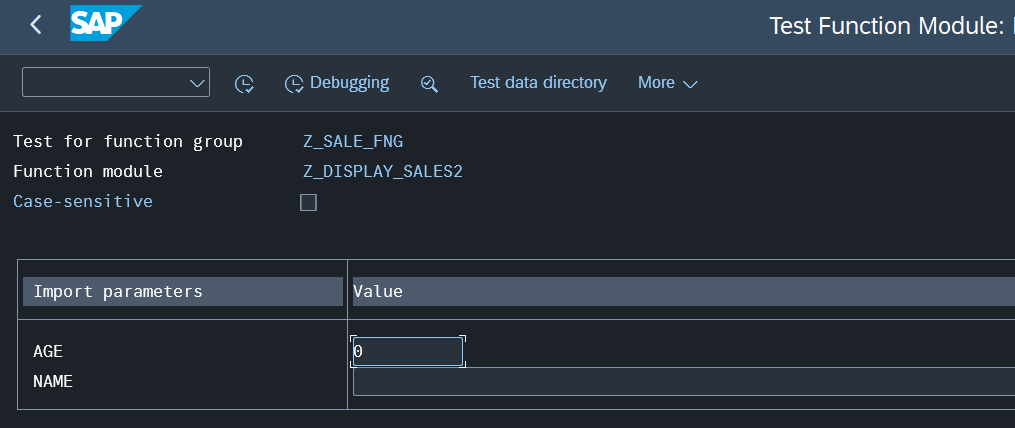 You can click again F8 to run it (it will show export/import data). and to view the output you can click Shift + F5
You can click again F8 to run it (it will show export/import data). and to view the output you can click Shift + F5
The Performance and View of Import and Export Data
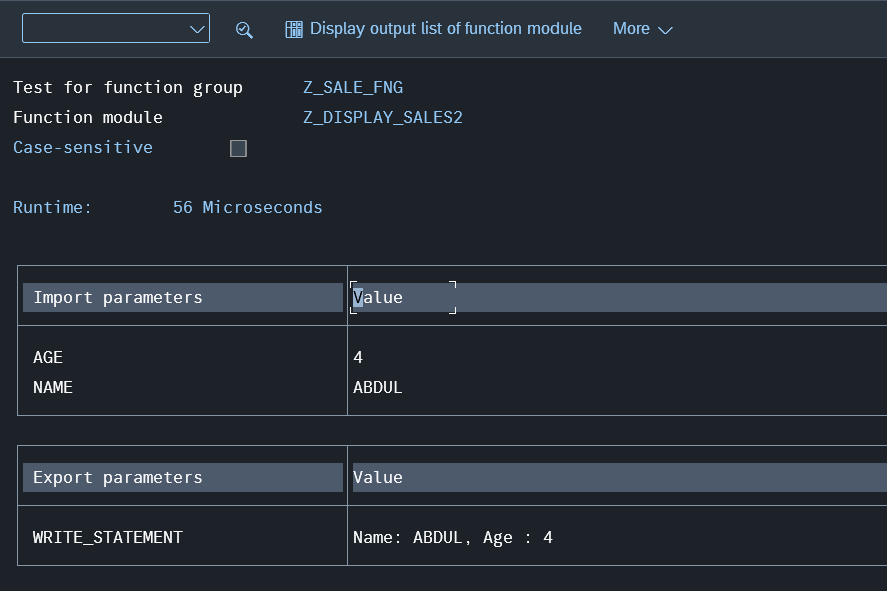
The Output
Calling Function Module
To call a function module you use CALL FUNCTION 'FUNCTION_NAME'.
For our function we called it like this.
" We define a variable to store our exported/returned value
DATA: writeSt TYPE STRING.
CALL FUNCTION 'Z_DISPLAY_SALES2'
EXPORTING
age = 10 " These will be sent to the function
name = 'Abdullah Bozaid' " These will be sent to the function
IMPORTING
WRITE_STATEMENT = writeSt. "This will store the WRITE_STATEMENT value inside our writeSt
OUTPUT
There is an important tool in the ABAP Environment. it is called Pattern. You can access it from the toolbar or using CTRL+F6
Pattern will prompt you with a dialog to choose function module.
What it will do is write the function call with all its parameters. so you dont have to remember what variables the function export or import..etc. You can fill what you need.
