Recent History of SAP ERP systems
Since 2015, SAP has been focusing on modernizing its ERP system to enhance its capabilities and user experience. Not only on the side of end users, but also in the backend. There are several changes that happen in the last decade.
SAP ECC (ERP Central Component)
SAP ECC has been the core ERP system for many years since its release in 2004. Till this day many companies still use it despite SAP announcing the end of support for ECC by 2027. There are key features of ECC that is drastically different from the new generation of SAP ERP systems:
- On-Premise: ECC is primarily an on-premise solution, meaning it is installed and run on the company's own servers and infrastructure.
- Database Agnostic: ECC can run on various databases such as Oracle, SQL Server, or newly SAP HANA.
- ABAP-based: ECC is built using the ABAP programming language, which is proprietary to SAP.
- Traditional User Interface: ECC uses the SAP GUI (Graphical User Interface), which is a desktop application with a more traditional and less user-friendly interface.
- Rely on Application Servers: ECC relies on application servers to handle business logic and processing.
Example of SAP GUI interface:
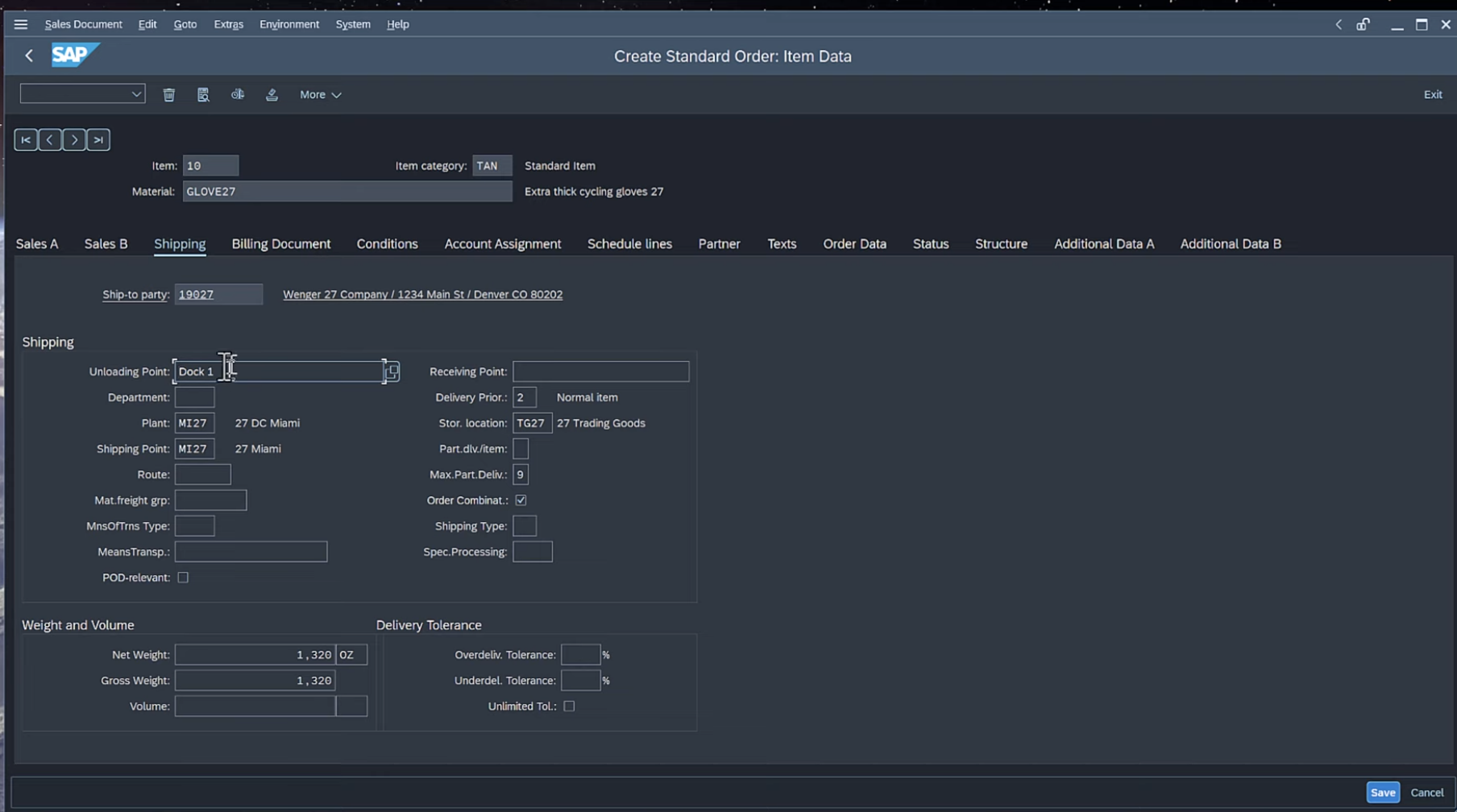
even though it has been updated over the years, it still looks very outdated compared to modern web applications. SAP GUI ran on desktop applications, and it was not web-based.
SAP S/4HANA
in 2015, SAP introduced S/4HANA, a replacement for ECC. Modernizing their ERP system UI/UX. S/4HANA utilize SAP HANA database, which is an in-memory database that provides high performance and real-time data processing. In addition, it is uses a SAPUI5 to develop its UI helping it achieve a modern web-based interface. Here are some key features/changes of S/4HANA:
-
Cloud and On-Premise: S/4HANA is available in both cloud and on-premise versions, providing flexibility for deployment. However, SAP is pushing to be only cloud-based in the future with private cloud.
-
Clean Core: S/4HANA emphasizes a "clean core" approach, minimizing customizations to the core system to facilitate easier upgrades and maintenance. Developers are encouraged to use extensions and side-by-side applications instead of modifying the core system (Will be discussed in detail later).
-
Fiori User Experience: S/4HANA uses the Fiori design principles, similar for example to Apple (IOS Components) or Google (Material Design) design principles.
It is a framework to build web applications. It is based on JavaScript, HTML5, and CSS3. It is open-source and free to use. It is used to build SAP Fiori applications. It is similar to other web frameworks like React, Angular, or Vue.js. Its greatest advantage is its seamless integration with OData
SAP Business Technology Platform (BTP)
Since 2015, SAP introduced many new products and services, to facilitate development and management of SAP applications and services, SAP, in 2021, introduced SAP BTP (Business Technology Platform). It is a cloud-based platform that provides a range of services and tools for building, deploying, and managing applications. In some sense, it is similar to AWS, Azure, or GCP. It has services that include more services. Like Google Cloud Platform (GCP) has an entire Cloud Platform "Firebase" within its suite.